Difference between revisions of "W12022Online"
(→Tutorials) |
(→MSc 2 (BK-CiTG-3ME) 2022: Interactive Furniture) |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=='''Grasshopper Conventions'''== | =='''Grasshopper Conventions'''== | ||
Revision as of 08:04, 18 January 2022
MSc 2 (BK-CiTG-3ME) 2022: Interactive Furniture
Grasshopper Conventions
Described here are some drawing conventions we use in the Robotic Building Lab for Grasshopper. The aim is to create clear organizational structures and descriptions of how and why a script is developed in a certain way so that it is easy to understand. A template using these conventions is provided here:
File:1.GH Conventions-GH Template.gh
Organisation
The Grasshopper scripts are organized according to certain principles considering the layout.
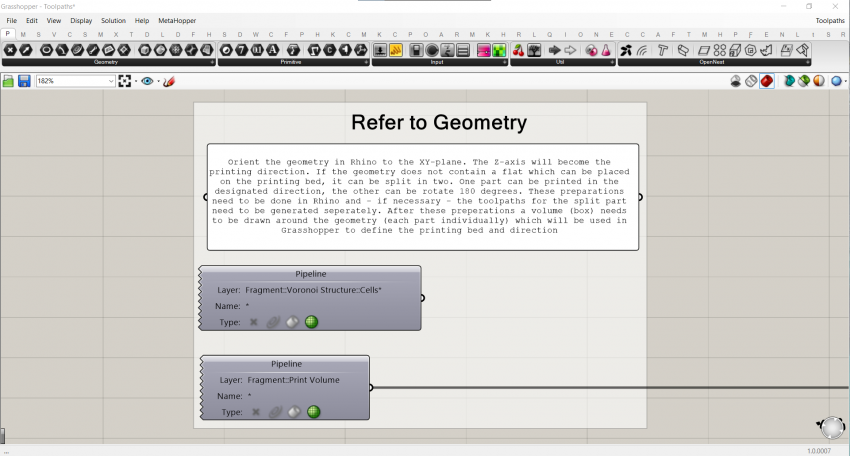
Every script starts with a title and abstract that contains a general description of the script does and for what purpose. Make sure to save the file while in this view so this is visible when the file is opened:
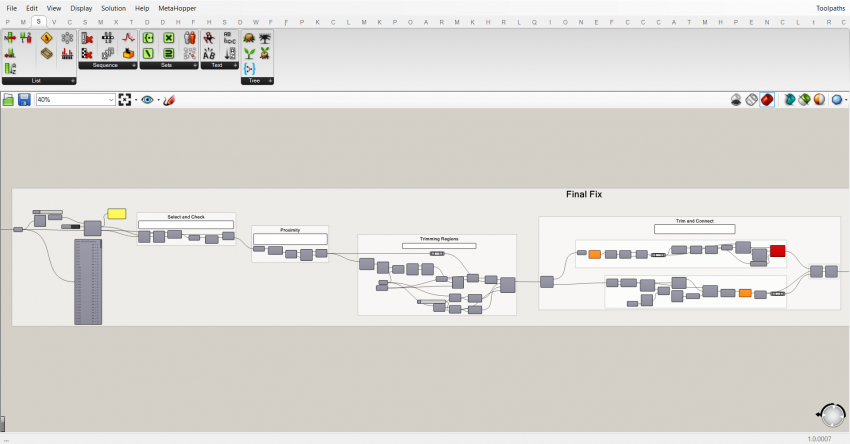
The components are organized and ordered in groups and subgroups. Every group has at least a title. If required it also contains a textual description in a panel. In general, the groups are colored white. The smallest groups are titled in the group header, a level above that by a scribble with font-size 25, and the main groups with a scribble with font-size 50. All the wires which reduce the readability of the script are set to display 'Hidden'.
The panels containing the textual descriptions are also white:
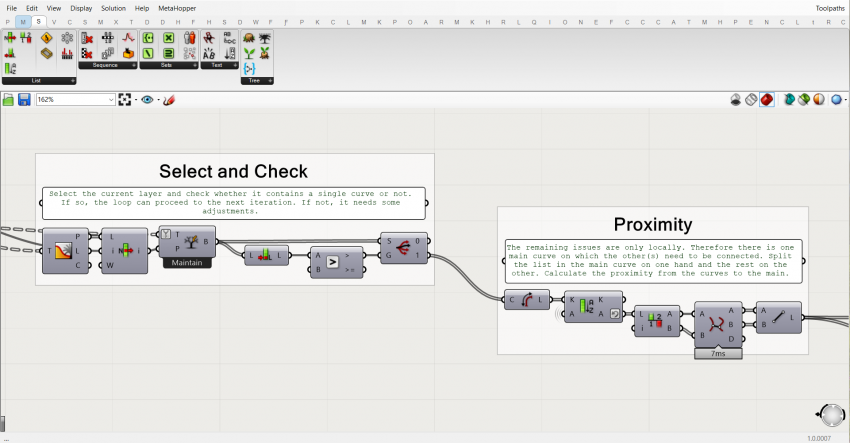
Data Management
Often the script is part of a sequence of scripts, each with a specific task. To create a fluid workflow and be sure the correct data is referred to, certain rules are maintained. Geometry is baked using the baking components of the plug-in Elefront. A layer and a name is assigned, so that the geometry is easy to be referred to in succeeding scripts and it is overwritten each time the component bakes.
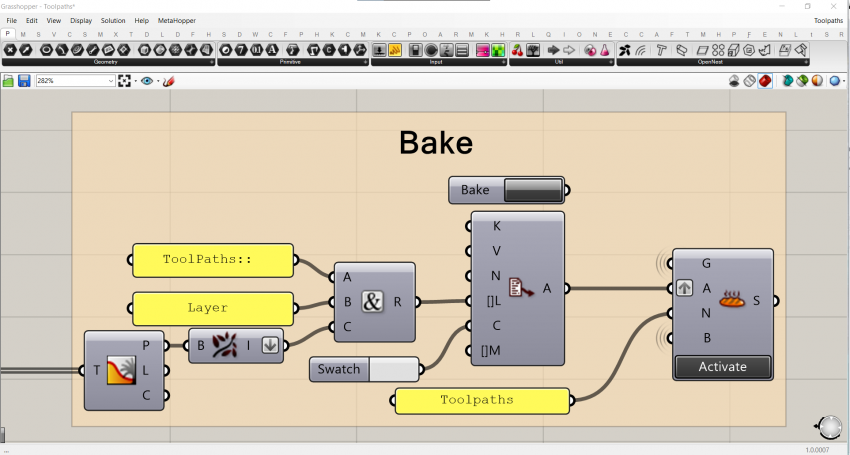
In this way, the geometry can be referred to using the geometry pipeline, and is updated accordingly. Always use the geometry pipeline and the combination between Rhino- and Grasshopper files, since internalizing geometry in a Grasshopper container greatly affects the speed of the script.