Msc1G4:Page3
Micro
Bewar Ahmed - Nino Schoonen
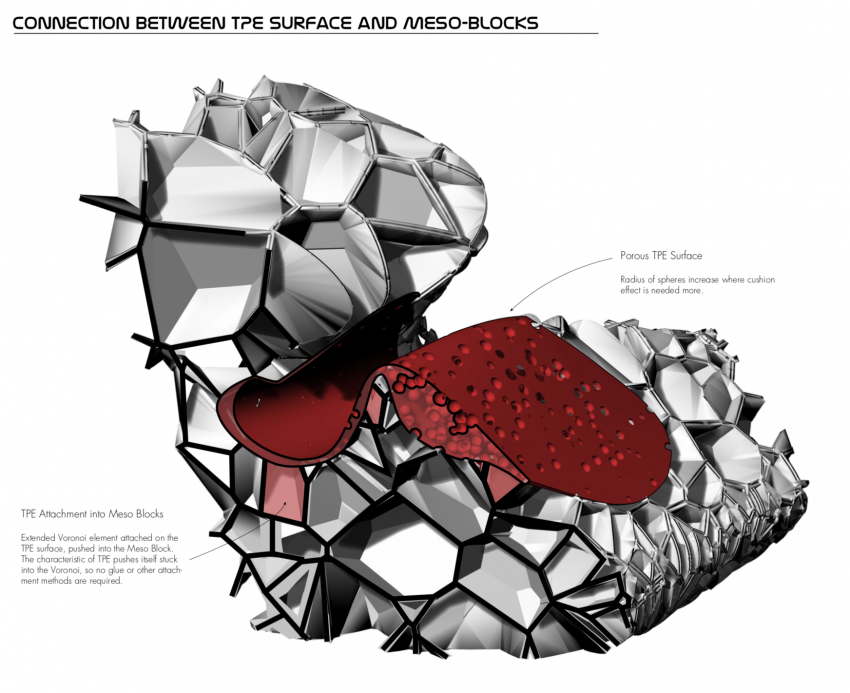
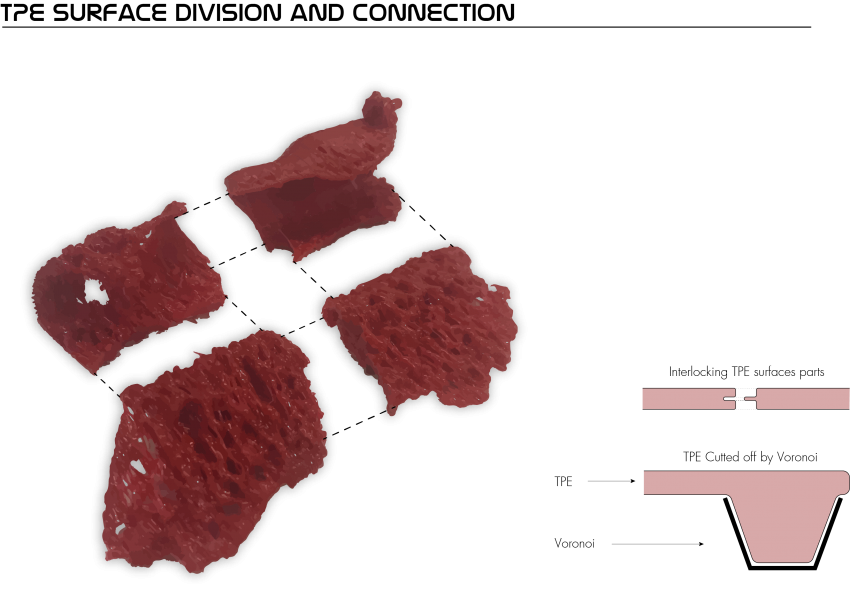
TPE Surface
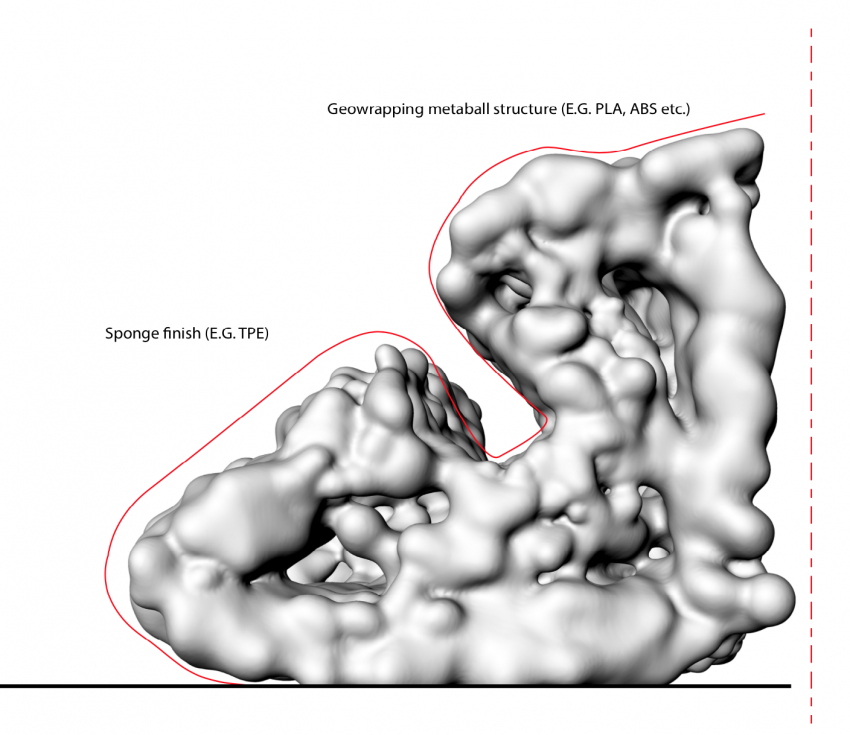
One of our main objectives for this research was to find a transition between structural material efficiency and using soft material where necessary. People doing excercises on the furniture should not be hurting themselves during the workout for example. Applying these soft surfaces only where they are required can save a lot of costs, as our chosen material: TPE filament (flexibility 85a) is more than four times more expensive than for example PLA filament. TPE has the characteristic quality of being able to deform a lot, without breaking itself over a long time. An alternative material with similar characteritics but even better lasting capabilities is Arnitel, yet this is twice as expensive as TPE.
Assembly
Design strategy
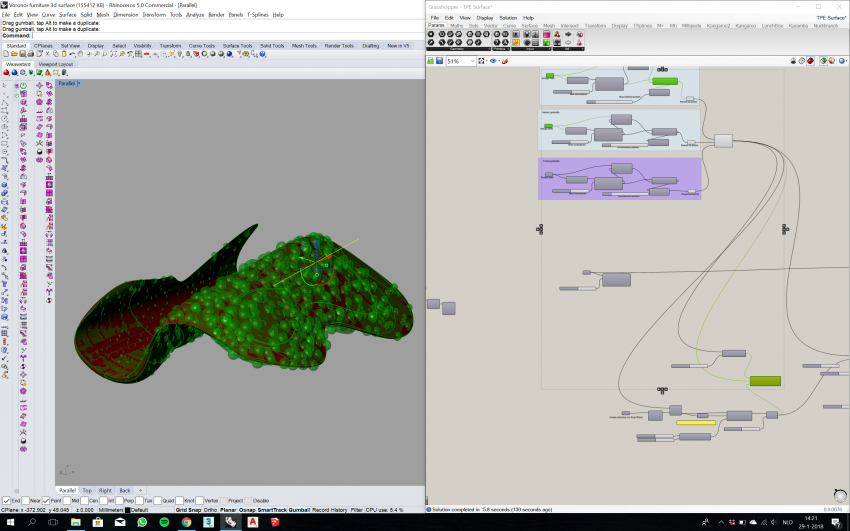
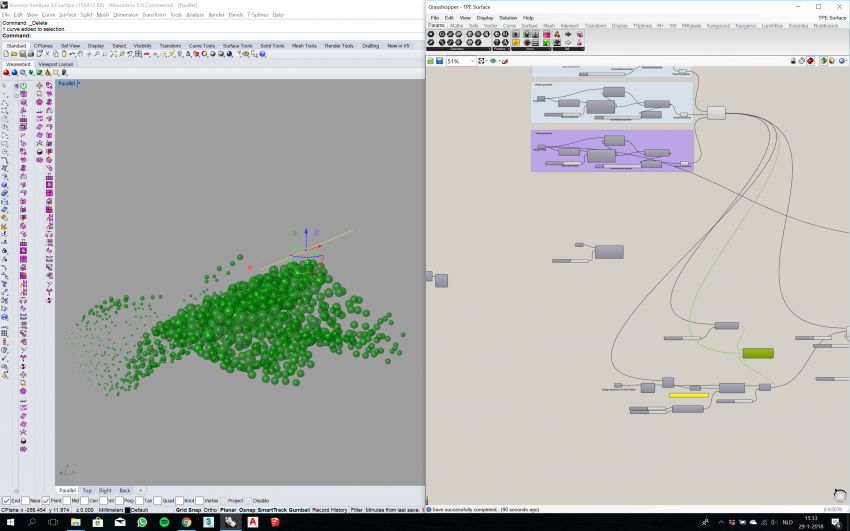
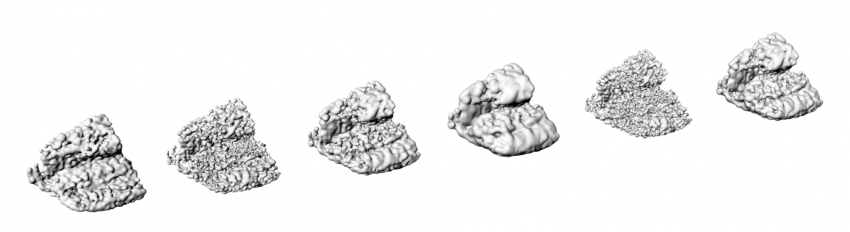
Assigning TPE Area's with T-Splines, optimizing density with different box clouds, making the area where more cushion effect is needed more dense populated, or almost not populated where no cushion effect is required.
Optimizing the Sphere-radius with attractor curves. Bigger Spheres increase the cushion effect.
Objective since workshop W3@TUD
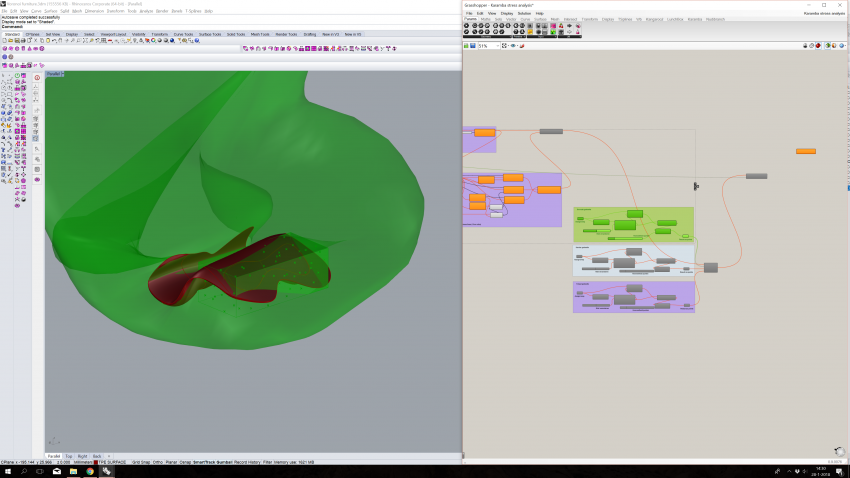
We've managed to script a load-bearing structure in Grasshopper, by manipulating point clouds with attractor/repelling curves. The result was a very dense Cocoon structure, obviously not optimal regarding material efficiency. This is the point where we've aimed for the objective of making an efficient transition between a load bearing structure, and soft cushion surface where that surface is required.